一、论文解读
论文:?Drost et al. Model Globally, Match Locally: Efficient and Robust 3D Object Recognition. CVPR, 2010. http://campar.in.tum.de/pub/drost2010CVPR/drost2010CVPR.pdf Model Globally, Match Locally?论文名字用 4 个词高度总结了 PPF 算法的精髓:“整体建模,局部匹配”。下面研读一下摘要(Abstarct):
[1] This paper addresses the problem of?recognizing free form 3D objects in point clouds.
第一句话表明论文的研究方向与问题:3D物体点云(free form)的识别
[2] Compared to traditional approaches based on?point descriptors, which depend on local information around points, we propose a novel method that?creates a global model description based on oriented point pair features and matches that model locally using a fast voting scheme.
第二句话既表明论文的创新点(与前人方法的区别),又用一句话总结本文的中心思想。 ·Model Globally:?creates a global model description based on oriented point pair features ·Match Locally:?matches that model locally using a fast voting scheme
[3] The?global model description?consists of all model point pair features and represents a mapping from the point pair feature space to the model, where similar features on the model are grouped together.
第三句话紧接着解释了什么是 global model description
[4] Such representation allows using much sparser object and scene point clouds, resulting in very fast performance.
第四句话说明这种 representation 的优点:稀疏采样,提升算法速度
[5] Recognition is done locally using an efficient voting scheme on a reduced two-dimensional search space.
第五句话表明如何实现 recognition:使用有效的投票机制在二维搜索空间里做局部匹配
[6] We demonstrate the efficiency of our approach and show its high recognition performance in the case of?noise, clutter and partial occlusion.
第六句话表明本文算法针对的场景问题:干扰、堆叠、部分遮挡
[7] Compared to state of the art approaches we achieve better recognition rates, and demonstrate that with a slight or even no sacrifice of the recognition performance our method is much faster then the current state of the art approaches.
第七句话说明通过与 SOTA 方法的对比,文中提出的方法既保证了高的识别率,又在不牺牲识别性能的情况下提升了算法的速度。 接下来看一下论文的算法:
1. Model Globally
首先定义两个词:scene?和?model?,scene 是我们测得的真实场景(点云),model 是物体的真实模型(点云)。
Both the scene and the model are represented as a finite set of oriented points, where a normal is associated with each point.
符号表示:
?points in the scene
?points in the model
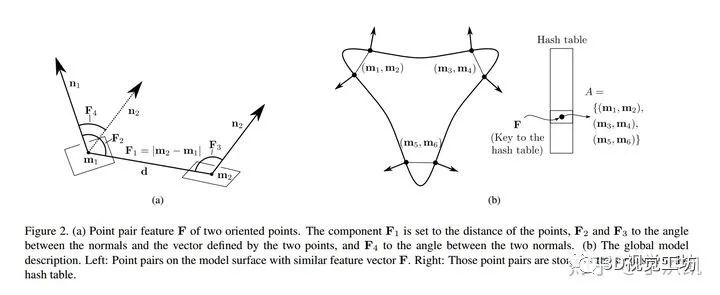
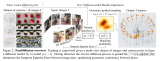
(1)Point Pair Feature (PPF) Model Gobally 的本质是通过定义 Point Pair Feature,来构建特征矢量的集合以及每个特征矢量对应的点对集,作为 Global Model Desciption。所以,首先先定义 PPF。 PPF 描述了两个有向点(oriented points)的相对位置和姿态。 假设有两个点??和?
?,法向量(normals)分别为?
?和?
?,?
?,则 PPF 定义为:
注:?
?为两个矢量的夹角,且?
?是非对称的。PPF 示意图见 Figure2.(a)。 有了 Point Pair Feature,就可以用其来定义 Global Model Description。 (2)Global Model Description 注:Global Model Description 是离线(in the off-line phase)构建的 先看原文:
The model is represented by a set of?point pair features?with similar?feature vectors?being grouped together.
实现方法: 第一步:计算 model 表面所有 point pairs 的特征矢量??,其中 distances 和 angles 分别以?
?和?
?的步长做采样; 第二步:构建哈希表(hash table),将具有相同 feature vector?
?的 point pair 放在一起,即哈希表的键(key )为 feature vector?
?,值(value)为具有相同特征矢量的点对集?
?,如 Figure2.(b) 所示。 ?
The global model description is a mapping from the sampled point pair feature space to the model.
2. Match Locally
当定义好全局模型描述(Global Model Description)后,就可以考虑局部匹配了。 All model features??that are similar to a given scene feature?
?can then be searched in constant time by using?
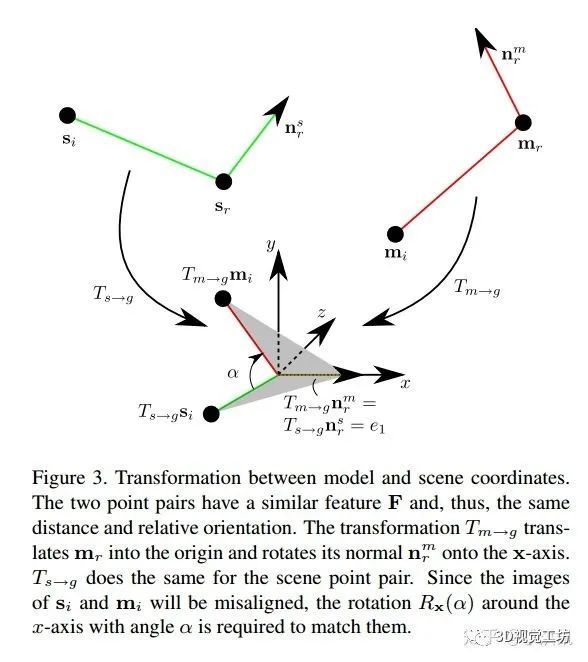
?as a key to access the hash table. (1)Local Coordinates 局部匹配的大概思路如下: ·从 scene 中选取任意一个参考点?
?,假设它在物体的表面上,若假设正确,则在 model 存在一个点?
?与?
?对应; ·将这两个参考点配准,需同时将点的位置和法向量对齐; ·让 model 绕?
?的法向轴转动一定角度与 scene 配准 由此看来,从 model space 到 scene space 的刚体变换可以由 model 中的一点和转动角度?
?来描述,将这个 pair?
?定义为 model 相对于参考点?
?的Local Coordinates 。 现在明确一下思路: ·给定参考点?
?,选取与 scene 点对?
?具有相似 fecture vector?
(same distance and relative orientation)的 model 点对?
?; ·通过变换矩阵?
?将?
?移动到 Local Coordinates 的原点,并且转动 model,使其法向轴?
?与 Local Coordinates 的?
?轴重合; ·同理,通过?
?对 scene 做相同操作; ·最后,将 model 中的一点?
?绕?
?轴转动?
?与?
?配准 通过上述描述,可以将从 model 到 scene 的 transformation 定义为:?
?,如 Figure 3 所示。
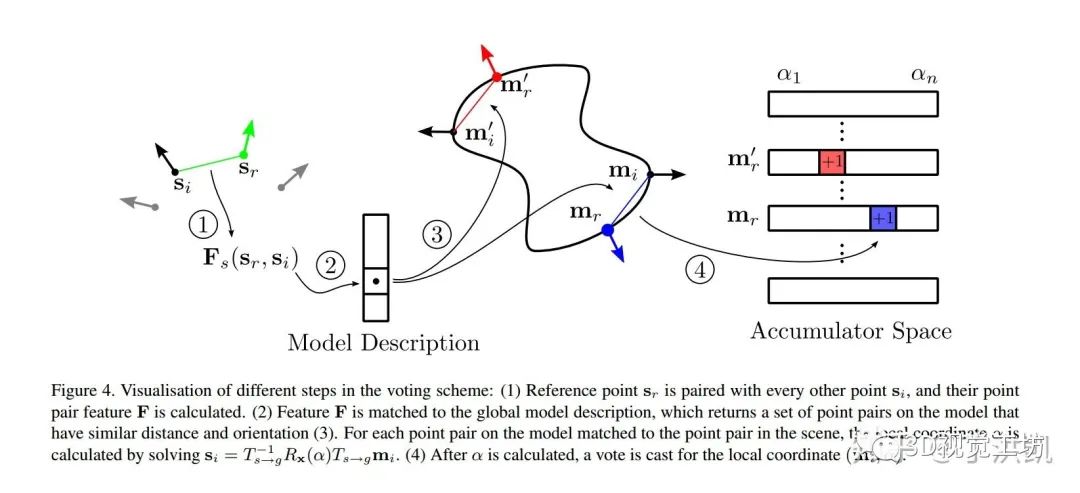
(2)Voting Scheme 现在我们可以将研究问题定义如下: ? 前面我们定义了 local coordinates,现在只需要通过一种方法找到最优的 local coordinates 使得 scene 中落在 model 表面的点最多,即可求出物体 pose。 论文通过投票机制实现,定义一个二维的 accumulator array,行(rows)数??为 model 采样点?
?的个数,列(columns)数?
?为按采样步长?
?的旋转角?
?的个数。 This accumulator array represents the discrete space of local coordinates for a fixed reference point. 具体实现: ·对于 scene 的参考点?
?,与 scene 中所有其他的点组成点对?
?,对每一个点对,计算?
?; ·将?
?作为 key,搜索 global model description 的哈希表,找到与?
?类似(distance & normal)的 model 特征矢量?
?和点对?
?; ·对于每个匹配的 model 点对?
?,通过之前的公式?
?可以算出旋转角?
?; ·对?
?与二维数组中离散?
?对应的位置投票(+1); ·全部计算完后,我们就可以得到参考点?
?的最大得票所对应的?
?和?
?,即最优的 local coordinates?
(3)Efficient Voting Loop 对每个点对都要求解??,为了加速计算,将?
?分解:?
?,这样就可以分别计算?
?和?
?了。 根据?
?和?
?,求得:
注: ·对于 model 或者 scene 中的每个点对,?
?都是唯一的 ·对于 model 中的每个点对,?
?可以在离线阶段求解 ·对于 scene 中的每个点对,?
?只需要算一次 (4)Pose Clustering 之前的算法基于我们的假设:参考点是在物体表面的。因此,我们需要在 scene 点云中采样多个参考点?
?,保证至少有一个参考点能在物体表面。 每个参考点可能返回多个位姿(投票相同),返回的位姿(retrieved poses)是否逼近 ground truth,取决于 model 和 scene 点的采样率和旋转角的采样。 我们对所有返回的位姿做聚类,每个 clutter 中位姿的位置、姿态的差异不超过设定的阈值,然后每个聚类的得分是其包含的所有位姿的总得分,找出得分最高的 clutter,则最终的位姿 为得分最高的 clutter 里面包含位姿的平均值。 如果场景中存在物体的多个实例,则会返回多个 clutters。
二、 OpenCV 实现
opencv_contrib 代码: https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib/tree/master/modules/surface_matching 文档 Documentation: https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/modules/surface_matching/doc/surface_matching.html 测试数据集: http://staffhome.ecm.uwa.edu.au/~00053650/recognition.html 注意: ·Mian数据集 ply 文件不含 normal 信息,需先计算法向量 ·可视化使用的 open3d(颜色渲染:z coordinate as color) 测试结果:
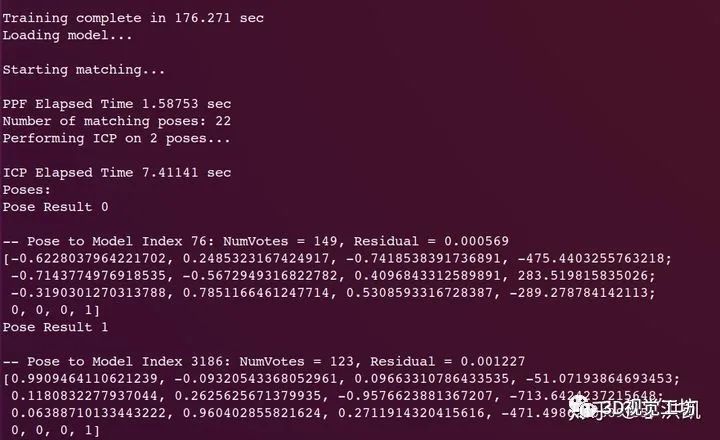
model scene 将经过位姿转换的 model 点云与 scene 点云叠加的效果: transformed model & scene
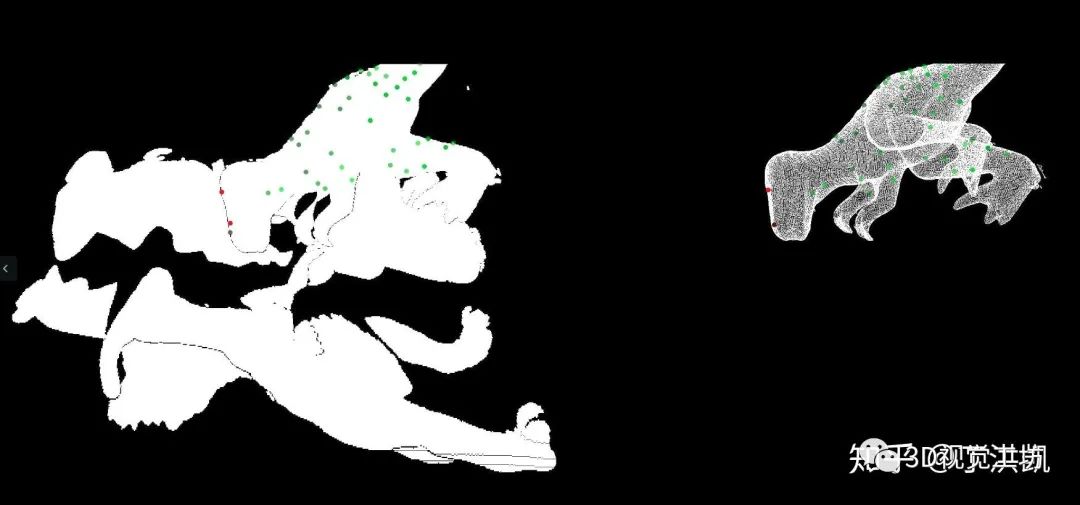
三、Matlab 实现
Github Project: https://github.com/guglu/ppf-matching 注: 代码中 mex 可执行文件应该是在 windows 平台下编译的,而我是在 ubuntu 系统中使用 matlab,所以需要重新编译一下,在 command line 中运行:
mex mex/computePPFmex.cpp mex mex/computePPFmex.cpp mex mex/MurmurHash3.cpp 运行 test_detector.m 脚本即可。 ? 结果:??
?

四、PCL 实现
PCL 中关于 PPF 的示例代码如下: https://github.com/PointCloudLibrary/pcl/blob/master/apps/src/ppf_object_recognition.cpp PCL 中定义了: PPFSignature:ppf 特征,定义在 point_types.hpp 中,是一种数据类型; PPFHashMapSearch:哈希表搜索模板类 PPFRegistration:ppf 配准模板类 建议在 PPF 之后用 ICP 迭代优化。
编辑:黄飞
 电子发烧友App
电子发烧友App


























评论