1?前言
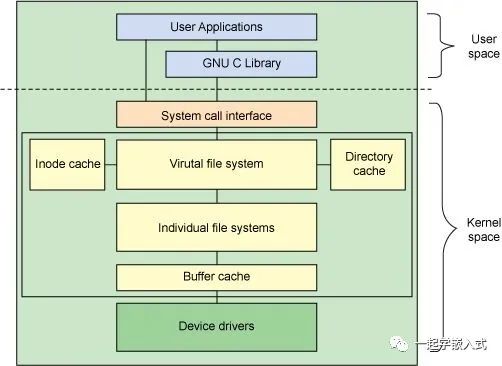
内核中有三个常用的伪文件系统:procfs,debugfs和sysfs。
procfs — The proc filesystem is a pseudo-filesystem which provides an interface to kernel data structures.
sysfs —?The?filesystem for exporting kernel objects.
debugfs — Debugfs exists as a simple way for kernel developers to make information available to user space.
它们都用于Linux内核和用户空间的数据交换,但是适用的场景有所差异:
procfs 历史最早,最初就是用来跟内核交互的唯一方式,用来获取处理器、内存、设备驱动、进程等各种信息。
sysfs 跟 kobject 框架紧密联系,而 kobject 是为设备驱动模型而存在的,所以 sysfs 是为设备驱动服务的。
debugfs 从名字来看就是为debug而生,所以更加灵活。
它们仨的挂载方式类似,做个实验:
$ sudo mkdir?/tmp/{proc,sys,debug}
$ sudo mount?-t proc nondev?/tmp/proc/
$ sudo mount?-t sys nondev?/tmp/sys/
$ sudo mount?-t debugfs nondev?/tmp/debug/
不过,默认情况下,它们分别挂载在/proc,/sys/,/sys/kernel/debug/。
下面简单介绍这三个文件系统的用法。在介绍之前,请记下他们的官方文档:
procfs — Documentation/filesystems/proc.txt
sysfs — Documentation/filesystems/sysfs.txt
debugfs — Documentation/filesystems/debugfs.txt
2?debugfs
API说明
struct?dentry?*debugfs_create_dir(const?char?*name,?struct?dentry?*parent)
struct?dentry?*debugfs_create_file(const?char?*name,?umode_t?mode,
struct?dentry?*parent,?void?*data,
const?struct?file_operations?*fops)
参考实例
drivers/base/power/wakeup.c:
/**
* wakeup_sources_stats_show - Print wakeup sources statistics information.
* @m: seq_file to print the statistics into.
*/
static?int?wakeup_sources_stats_show(struct?seq_file?*m,?void?*unused)
{
struct?wakeup_source?*ws;
seq_puts(m,?"name active_count event_count wakeup_count "
"expire_count active_since total_time max_time "
"last_change prevent_suspend_time ");
rcu_read_lock();
list_for_each_entry_rcu(ws,?&wakeup_sources,?entry)
print_wakeup_source_stats(m,?ws);
rcu_read_unlock();
return?0;
}
static?int?wakeup_sources_stats_open(struct?inode?*inode,?struct?file?*file)
{
return?single_open(file,?wakeup_sources_stats_show,?NULL);
}
static?const?struct?file_operations wakeup_sources_stats_fops?=?{
.owner?=?THIS_MODULE,
.open?=?wakeup_sources_stats_open,
.read?=?seq_read,
.llseek?=?seq_lseek,
.release?=?single_release,
};
static?int?__init wakeup_sources_debugfs_init(void)
{
wakeup_sources_stats_dentry?=?debugfs_create_file("wakeup_sources",
S_IRUGO,?NULL,?NULL,?&wakeup_sources_stats_fops);
return?0;
}
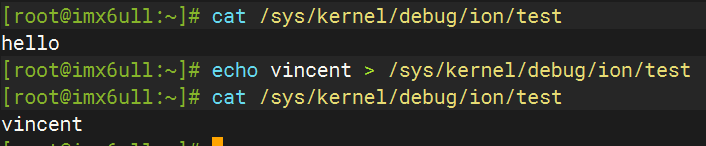
创建完的接口
/sys/kernel/debug/wakup_sources
给接口添加多级目录
上述接口直接创建在?debugfs?根目录(/sys/kernel/debug)下,所以?debugfs_create_file的parent参数被设置成了NULL,如果要加一级目录,则可以先用debugfs_create_dir?创建一级目录,例如,要创建:/sys/kernel/debug/power/wakeup_sources?的话,则需要:
struct?dentry?*power;
int?err?=?-ENOMEM;
power?=?debugfs_create_dir("clock",?NULL);
if?(!power)
return?err;
wakeup_sources_stats_dentry?=?debugfs_create_file("wakeup_sources",
S_IRUGO,?power,?NULL,?&wakeup_sources_stats_fops);
3?procfs
proc_mkdir?用法跟?debugfs_create_dir?几无差异。
API说明
static?inline?struct?proc_dir_entry?*proc_mkdir(const?char?*name,?struct?proc_dir_entry?*parent)
static?inline?struct?proc_dir_entry?*proc_create(const?char?*name,?umode_t?mode,
struct?proc_dir_entry?*parent,?const?struct?file_operations?*proc_fops)
参考实例
在上面例子的基础上,可以添加如下语句:
static?int?__init wakeup_sources_debugfs_init(void)
{
proc_create("wakelocks",?S_IFREG?|?S_IRUGO,?NULL,?&wakeup_sources_stats_fops);
return?0;
}
创建后的接口
/proc/wakelocks
给接口添加多级目录
这样创建的接口用起来跟?/sys/kernel/debug/wakeup_sources?没有任何差异,类似地,如果要加一级目录,例如?/proc/power/wakelocks,则可以:
struct?proc_dir_entry?*power;
int?err?=?-ENOMEM;
power?=?proc_mkdir("power",?NULL);
if?(!power)
return?err;
proc_create("wakelocks",?S_IFREG?|?S_IRUGO,?power,?&wakeup_sources_stats_fops);
4?sysfs
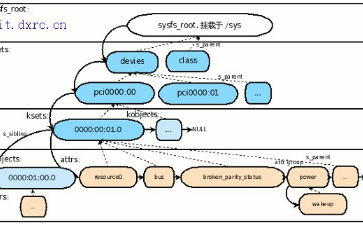
在?sysfs?中,有另外一个常见用法,那就是在一个 kobject 对应的目录下创建一个符号(属性文件)指向另外一个 kobject 对应的目录,通常这个是为了方便记忆和访问。这个API是?sysfs_create_link。
这种创建符号链接方法其实有一个很特殊的实例,那就是在驱动模型里头,有一个?class?的概念,它把挂在不同总线上,但是实现类似功能的设备进行归类,比如说?input类,backlight?类等。
如果设备属于一个现存的类,比如?backlight,那么可以用?backlight_device_register?创建,如果是?I2C?设备,会先在I2C下创建?sysfs?访问节点,并创建一个符号链接到?backlight?类所属的目录下。
当然,如果没有找到设备能挂的直观的类,也可以用?class_create?创建类,设备类通常会有一组默认的设备操作接口,例如?backlight?类有?bl_device_attributes,如果要创建更多的设备特定的节点,可以用?device_create_file?或者?device_add_groups?创建节点或者节点群。
API说明
struct?kobject?*kobject_create_and_add(const?char?*name,?struct?kobject?*parent)
int?sysfs_create_file(struct?kobject?*?kobj,?const?struct?attribute?*?attr)
static?inline?int?sysfs_create_link(struct?kobject?*kobj,?struct?kobject?*target,?const?char?*name)
int?device_create_file(struct?device?*dev,?const?struct?device_attribute?*attr)
参考实例
在?/sys/power?下创建一个 wakelocks 节点,用于读/写一个字符串。
static?char?test_str[11];
static?ssize_t?show_wakelocks(struct?kobject?*kobj,?struct?attribute?*attr,?char?*buf)
{
int?ret;
ret?=?snprintf(buf,?10,?"%s ",?test_str);
return?ret;
}
static?ssize_t?store_wakelocks(struct?kobject?*kobj,?struct?attribute?*attr,
const?char?*buf,?size_t?count)
{
int?tmp;
ret?=?sscanf(buf,?"%10s",?test_str);
if?(ret?!=?1)
return?-EINVAL;
return?count;
}
define_one_global_rw(wakelocks);
static?int?__init wakelocks_init(void)
{
int?ret;
ret?=?sysfs_create_file(power_kobj,?&wakelocks.attr);
}
创建后的节点
/sys/power/test_node
给接口添加多级目录
咱们上面其实已经把 test_node 创建在?/sys/power?目录下,而非根目录?/sys?下,而参数 power_kobj 为内核已经在?kernel/power/main.c?创建的kobject对象。
struct?kobject?*power_kobj;
power_kobj?=?kobject_create_and_add("power",?NULL);
if?(!power_kobj)
return?-ENOMEM;
5?小结
通过比较发现,上述三个文件系统的 API 用法类似,而其中?debugfs?和?procfs?几乎有相同的参数,用的主要结构体是?struct file_operations,蛮多操作可以用?seq_*?家族的函数来实现。而?sysfs?则用到比较简单一些的?struct global_attr?结构体。对于提供给用户空间的节点,都可以轻松实现读写操作。
在创建目录方面,debugfs?和?procfs?类似,且比较简单。而?sysfs?要创建一级目录,需要先创建一个 kobject 对象。
为了简化设备模型依据总线创建的访问节点路径,sysfs?提供了API用于创建更简易的符号链接,可以创建到自己指定的目录下,也可以用设备类(Class)提供的API创建到设备类所属的目录下。
对于?sysfs,由于?kobject?与?device?的一对一依存关系,也可以直接用?device_create_file?来创建节点。
?
 电子发烧友App
电子发烧友App
























评论